Reform Index is +1.0 points for the period from August 2 to August 15, 2021, with possible values ranging from -5.0 to +5.0. In the previous round, the index was +0.9 points.
Chart 1. Reforms Index Dynamics
Chart 2. Reforms Index and its components in the current round
Law on the resumption of the work of the High Qualifications Commission of Judges, +2.0 points
The High Qualifications Commission of Judges of Ukraine (HQC) is a collegial body of judicial branch governance responsible for the selection and assessment of judicial candidates. After the HQC recommends judges for appointment, they should also be approved by the High Council of Justice.
This body has not been operating since 2019. The public had no trust in this body’s activities because it had repeatedly recommended corrupt judges for appointment. According to experts, one of the reasons for this problem was the principles of forming the HQC. Judges constituted two thirds of the Commission, but it turned out that they were not ready to provide an objective assessment and dismiss their colleagues. Specifically, the idea of cleaning up the judicial system failed to be implemented. Therefore, Parliament passed a law dissolving the HQC.
Law 1629-IX of July 13, 2021, provides a new set of principles to form the HQC.
Information about the Reforms Index project, the list of Index experts and the database of the regulations assessed are available here.
Law on the procedure for electing members of the High Council of Judges, +2.0 points
The High Council of Justice (HCJ) is responsible for appointing and dismissing judges, as well as for disciplining them for wrongdoing. This body plays a key role in the successful implementation of judicial reform. However, the current composition of the HCJ has failed in this task. Therefore, the question of “relaunching” this body arose.
Law 1635-IX of July 14, 2021, introduced a preliminary assessment of potential candidates to HCJ during the selection process and initiated a one-time assessment on whether the current members meet the criteria of professional ethics and integrity.
Law on strengthening the responsibilities of bank management bodies for decision-making, +2.0 points
Law 1587-IX of June 30, 2021, brought the legislation on corporate governance in banks closer to EU standards.
In particular, it requires that the bank founders and owners of substantial parti provide the NBU with all the documents available affirming that its good standing and financial condition are in line with the requirements of the law.
The law clearly defined the powers of banks’ supervisory boards. The exclusive competence of the supervisory board includes assessing the activities of the bank’s committees and board, defining the remuneration policies, approving and monitoring compliance with the ethics code, approving the bank’s conflict of interest management policy, etc.
The law also expands the powers of the NBU to assess whether the bank’s board and management have appropriate qualifications and ability to ensure effective management. Now, the NBU can require that the composition of the board or management of the bank be changed if these bodies’ current composition cannot ensure effective management.
Besides, the law made some adjustments regarding the NBU Council by reducing its opportunities for interference in the work of the management board and increasing the salaries of its members. The law also introduced an additional position of NBU Board member – it will now be seven of them, not six.
The law improving the mechanisms for withdrawing banks from the market and satisfying creditors’ claims, +1.8 points
Practice has shown that bank executives can consciously make decisions harming the financial condition of banks for their own benefit. Particularly, they lend to individuals associated with the bank on non-market terms, buy “junk” securities, withdraw liquid assets from collateral for loans, etc. The current legislation calls for such individuals’ liability if they harm the bank’s financial condition. However, in many cases, compensation mechanisms do not make it possible to recover damages in practice.
Law 1588-IX of June 30, 2021, tries to tackle this issue. It allows the Deposit Guarantee Fund (DGF) to initiate proceedings in foreign and international courts to recover damages caused to the bank as a result of the nationalization or expropriation of bank property. The law provides grounds for compensation by individuals who caused damage to the bank or benefited from such action. The possibility of voluntary compensation for such damage is also provided.
The law also allows the DGF to apply to foreign and international courts in the event of requisitioning, destroying or devaluing bank assets due to hostilities and armed conflicts.
Law on the digital economy, +1.5 points
Law 1667-IX of July 15, 2021, introduces the legal regime of Diia City for ІТ industry.
This legal regime provides special taxation, employment and regulation incentives for companies that are residents of Diia City.
The law stipulates that a Diia City resident company can hire employees based on so-called gig contracts. The law defines such employees as gig specialists. Unlike the agreements for the provision of services that companies normally conclude with their private entrepreneur employees, a gig contract can specify set working hours and the time off work.
To become a Diia City resident, the average monthly salary of company employees and gig specialists must be at least EUR 1,200, with their average number being at least 9 people.
The law also defines the list of agreements that can be concluded by Diia City residents:
- non-disclosure agreements that a specialist concludes with the resident, undertaking not to disclose trade secrets or any other confidential information of the resident,
- agreements on refraining from competing, according to which, during the term of the agreement, a specialist has an obligation to refrain from competing, concluding contracts with other companies or owning a stake in companies engaged in competitive activities,
- loan agreements with the alternative obligation when, at the request of the creditor as fulfillment of the alternative obligation, the debtor is obligated to include them among the debtor’s participants or to increase their share in the authorized capital.
It is expected that the next step in the implementation of the Diia City regime will be changes to the Tax Code.
Amendments to the law on the National Agency of Ukraine for Detection, Search and Management of Assets, +1.0 points
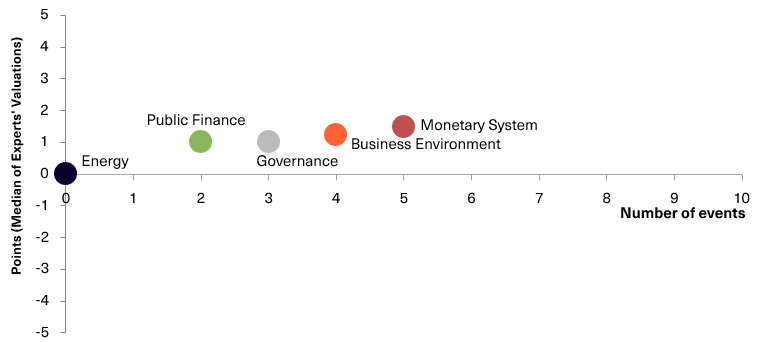
Chart 3. Value of Reforms Index components and number of events
Reforms Index from VoxUkraine aims to provide a comprehensive assessment of reform efforts by Ukraine’s authorities. The Index is based on expert assessments of changes in the regulatory environment in five areas:
- Governance
- Public Finance
- Monetary system
- Business Environment
- Energy
Attention
The author doesn`t work for, consult to, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and have no relevant affiliations